Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as one of the most captivating and transformative technologies of our era. From powering virtual assistants to guiding self-driving cars, AI has seamlessly integrated into our lives. But what exactly is AI, and how does it function? Discover the fundamental concepts of AI in our ‘AI Essentials 101‘ course. Explore how AI works and its real-world applications. This article delves into the intricacies of AI, exploring its underlying principles, components, and real-world applications.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
What is Artificial Intelligence?
At its core, Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, enabling them to learn, reason, and make decisions. It’s the fusion of data, algorithms, and computing power that empowers systems to perform tasks that previously demanded human intelligence.
The Evolution of AI: From Symbolic Logic to Machine Learning
The journey of AI began with symbolic logic and rule-based systems, but it truly flourished with the emergence of machine learning. This shift allowed AI models to learn patterns from data, leading to the development of narrow AI (focused on specific tasks), general AI (with human-like cognitive abilities), and the theoretical concept of superintelligent AI.
The Building Blocks of AI
Machine Learning at the Core
Machine learning serves as the heart of AI, enabling systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time. This process mirrors human learning, albeit at an astonishing speed and scale.
Neural Networks: Mimicking the Human Brain
Neural networks, inspired by the human brain’s neural connections, are key players in AI. They consist of interconnected nodes that process and transmit data, allowing AI models to recognize patterns, make decisions, and even create art.
Data Collection and Preprocessing: Fueling the AI Engine
AI’s effectiveness hinges on quality data. Data collection and preprocessing involve gathering relevant information and refining it for model training, ensuring that the AI engine learns from accurate and representative data.
Training and Optimization: Fine-Tuning the Model
Training an AI model involves exposing it to vast datasets and iteratively adjusting its parameters to minimize errors. Optimization techniques enhance the model’s performance, making it adept at tasks like image recognition or language translation.
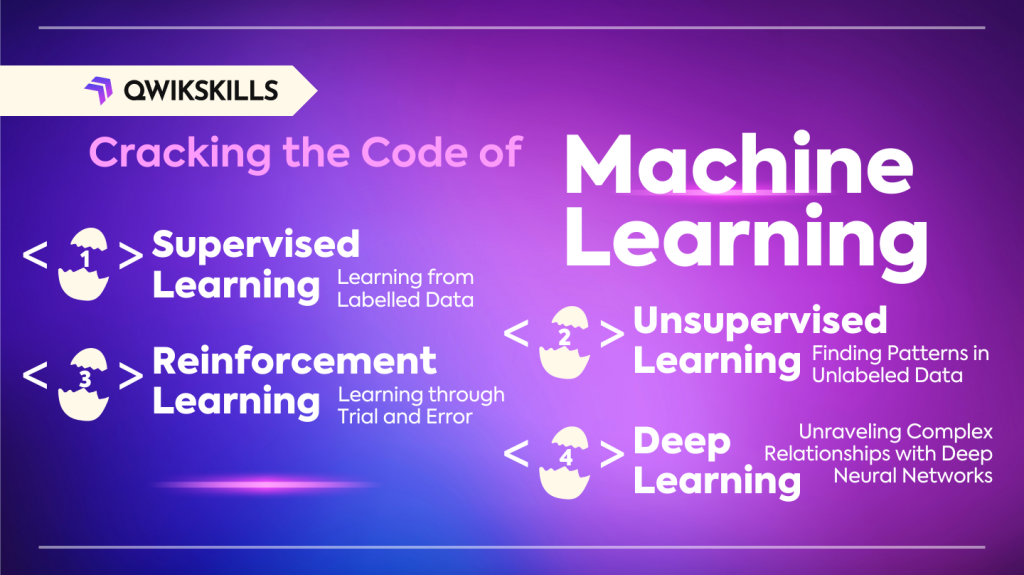
Cracking the Code of Machine Learning
Supervised Learning: Learning from Labeled Data
In supervised learning, models learn from labeled examples, making predictions or classifications based on past data. This is like teaching a child through examples and letting them generalize from there.
Unsupervised Learning: Finding Patterns in Unlabeled Data
Unsupervised learning involves discovering hidden patterns within unlabeled data. It’s akin to uncovering new insights from a vast collection of unsorted puzzles pieces.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning through Trial and Error
Reinforcement learning mimics how humans learn by trial and error. An AI agent interacts with an environment, receiving rewards or penalties for its actions, eventually learning to make optimal decisions.
Deep Learning: Unraveling Complex Relationships with Deep Neural Networks
Deep learning involves intricate neural networks with multiple layers. Just as we gain deeper insights by exploring multiple layers of a topic, deep learning extracts intricate features from data for enhanced understanding.
NLP: The Language of AI
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Explained
NLP endows machines with the ability to comprehend, interpret, and generate human language. This enables applications like chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis.
Sentiment Analysis: Gauging Emotional Tone
Sentiment analysis deciphers the emotional tone in text. It’s like gauging the mood of a conversation, which helps businesses understand customer feedback.
Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying Entities in Text
NER identifies specific entities (names, dates, locations) within text. Think of it as extracting characters’ names from a novel to understand their roles.
Language Generation: From Chatbots to Content Creation
Language generation enables machines to produce human-like text. This ranges from chatbots that engage in conversation to algorithms crafting articles like this one.
Computer Vision: Seeing Through AI Eyes
How Computer Vision Empowers AI
Computer vision enables machines to process and interpret visual information, much like how our eyes and brain collaborate to understand the world.
Object Detection: Spotting and Classifying Objects
Object detection allows AI to identify and classify objects within images. It’s like an AI-powered detective spotting items in a picture.
Image Segmentation: Understanding Image Components
Image segmentation divides images into segments, pinpointing boundaries and areas of interest. It’s like dissecting a picture into smaller, understandable parts.
Facial Recognition: Unveiling Identity with AI
Facial recognition technology identifies and verifies individuals based on their facial features. It’s akin to unlocking your phone with a glance.
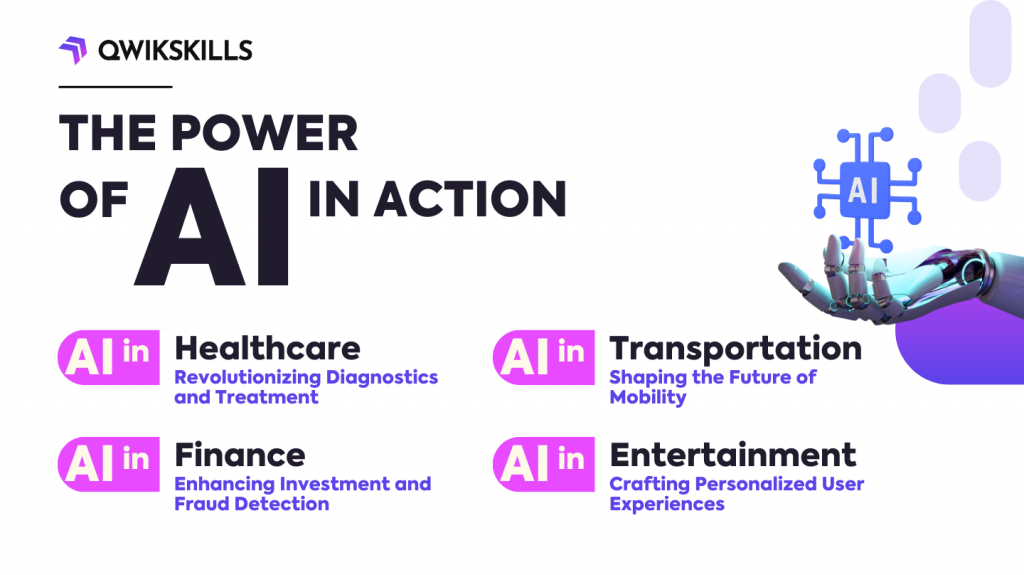
The Power of AI in Action
AI’s influence spans diverse domains, reshaping industries and experiences.
AI in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Diagnostics and Treatment
AI aids medical professionals in diagnosing diseases and designing treatment plans by analyzing vast patient data. It’s like having a team of doctors with encyclopedic knowledge.
AI in Finance: Enhancing Investment and Fraud Detection
In finance, AI predicts market trends, manages portfolios, and detects fraudulent transactions. It’s akin to having a financial advisor with impeccable instincts.
AI in Transportation: Shaping the Future of Mobility
AI guides self-driving cars, optimizing routes and preventing accidents. It’s like having a chauffeur who knows every road and traffic pattern.
AI in Entertainment: Crafting Personalized User Experiences
AI tailors entertainment experiences, from personalized playlists to movie recommendations. It’s like a virtual DJ curating tunes just for you.
Ethical and Societal Implications of AI
Bias and Fairness: Addressing AI’s Prejudices
AI can inadvertently amplify biases present in its training data. Ensuring fairness is like scrutinizing a jury selection to prevent biases from affecting verdicts.
Job Disruption: Navigating the Future of Work
As AI automates tasks, some jobs might evolve, while others could become obsolete. Adapting to this change is like adjusting to new tools in a rapidly evolving workplace.
Privacy Concerns: Balancing Innovation and Data Protection
AI’s hunger for data raises concerns about privacy. Balancing innovation with data protection is like ensuring the curtains are drawn while you innovate in the comfort of your home.
AI Regulation: Charting a Path for Responsible AI Development
Governments and organizations aim to regulate AI development, striking a balance between progress and ethical considerations. It’s like drafting road rules for the AI highway.
Semantically Similar FAQs
- What is the underlying principle behind AI technology? AI technology is grounded in the replication of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to learn from data, adapt to new information, and make decisions based on patterns.
- How does machine learning contribute to AI’s capabilities? Machine learning equips AI with the ability to improve its performance on tasks by learning from data, allowing it to uncover intricate patterns and relationships.
- What are the risks associated with biased AI algorithms? Biased AI algorithms can perpetuate prejudices present in training data, resulting in discriminatory outcomes that impact decision-making and fairness.
- Can AI truly replicate human creativity and problem-solving? While AI can simulate certain aspects of human creativity and problem-solving, achieving true replication of human cognitive abilities remains a complex challenge.
- How can industries adopt AI without causing significant job losses? Industries can adopt AI responsibly by integrating it into tasks that enhance human capabilities, thereby creating symbiotic relationships between AI and human workers.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence, born from the intersection of data, algorithms, and computing power, has revolutionized the way we live and work. Its journey from symbolic logic to sophisticated machine learning has yielded remarkable progress. From healthcare to finance, AI’s transformative impact is undeniable, but it comes with responsibilities. As we stride into the AI-powered future, ensuring ethics, fairness, and balance will be crucial to maximizing its benefits while minimizing its pitfalls.
Ready to dive into the world of AI? Explore QwikSkills for expert-led courses in Artificial Intelligence. From machine learning to NLP, master the tech that’s shaping our future! Start your AI journey today.